Image Source: Pixabay
A CNC machine can create highly accurate parts and products. It can produce 2D vector or 3D solid part CAD design models and geometries.
CAM software then converts these designs into a CNC programming language called G-code that machines can understand. There are also auxiliary function code (M-code) programs that control the ancillary functions of the machine.
CNC Machining
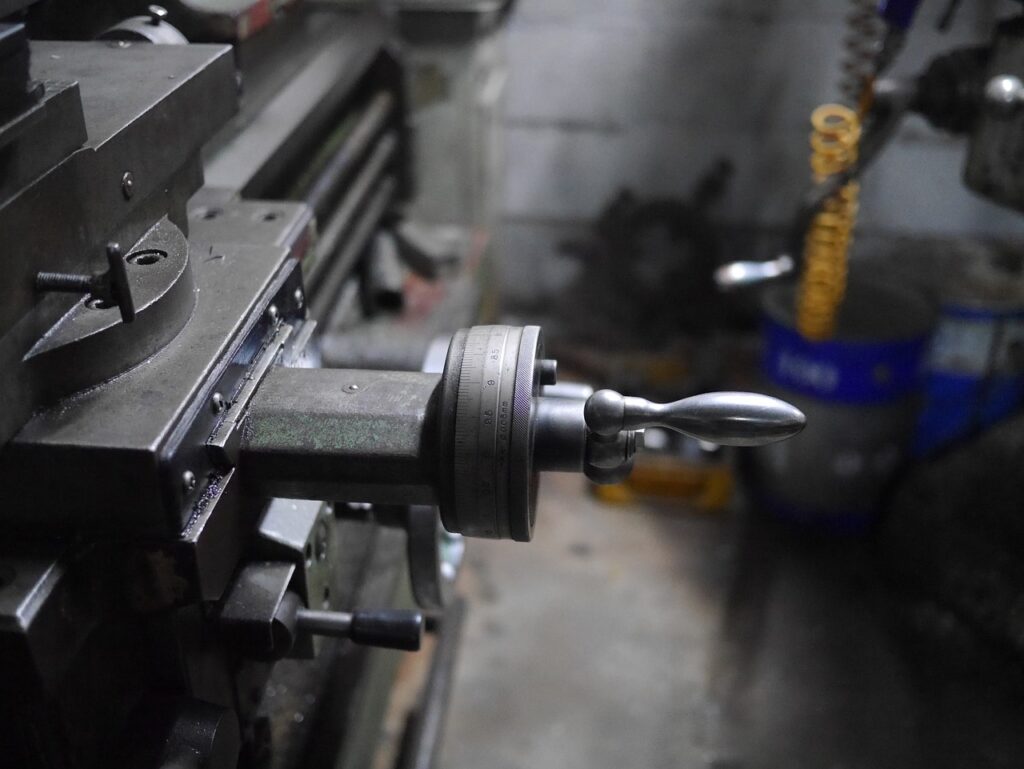
CNC machining is an automated process that uses precise machinery to create custom-designed parts and components. It allows manufacturers to produce accurate, consistent results and complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to make by hand. The resulting products are used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
The process begins with a 3D computer model of the part. The model determines the dimensions and properties of the finished part. Then, the model is translated into digital instructions, or G code, using a specialized CAM software program. The G-code tells the machine how to manipulate the tool and workpiece to achieve the desired shape.
Once the G-code is loaded, the operator prepares the machine for manufacturing. This may involve affixing the material onto machine spindles or into workholding devices. They must also attach the required tools and tooling to the machine, and load the correct cutting trajectories for each operation. This preparation is called setup, and it must be completed before the machine can begin producing the part.
Once the machine is ready, the operator runs the CNC program. The machine will then start cutting and drilling the material as per the instructions in the program. The machine will only stop once the program is finished or in the event of an unexpected error or power outage.
CNC Programming
CNC programming is the process of creating instructions that a machine uses to create a part. This is accomplished using a computer program that generates code for directing the machine’s tools or laser cutter. The program includes technological data and geometric data that tell the machine what functions to perform and how to make cuts. The program also specifies the machine’s feed rates and speeds.
This programming process can be lengthy and complicated, requiring a skilled programmer. The first step is to create a 2D or 3D model of the final design in CAD software. The CAD model is then translated into G code, which the CNC machine can read and follow.
The machine then moves around the workpiece, cutting and shaping it according to the g-code instructions. This is done in a variety of ways, including turning, which involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool shapes it; drilling, which produces holes with precision and accuracy; and laser cutting, which uses high-energy lasers to cut materials like metals and plastics.
When creating a CNC program, it’s important to consider the different properties of your material. For example, some metals are harder or softer than others. These differences might require a modification in the program to ensure better performance and consistency. In addition, it’s important to set up “Work Coordinates,” which determine how the machine refers to a particular point in the program.
CNC Setup
CNC machines can make a variety of shapes that are difficult to create by hand. They can also cut to a precise level of accuracy. For example, they can create a gear with a diameter that is only a few thousandths of an inch. This allows for an automated process that can make a large number of identical parts, saving time and money.
Before machining can begin, the CAD design must be converted to a format that the machine can understand. This is done using a computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) program, which extracts the geometry of the part and converts it into digital programming code that can be read by the CNC machine. The resulting code is known as G code, and it tells the machine where to move in terms of coordinates. It can also control other machine functions, such as spindle speed and coolant flow.
Once the G code is ready, the machine can be loaded and positioned for a first run. This can be done manually or with the help of a machine data platform that offers direct download to the equipment. The machine is then calibrated based on documented and standardized work instructions.
It is important to minimize setup times when using a CNC machine. This can be done by identifying and timing all elements that impact setup times. It is also possible to stage cleaning supplies, tools and blanks in kits or carts for use before each task, to reduce the time it takes to load them.
CNC Operation
CNC operation refers to the process of using computerized controls and precise machinery to cut, shape, and produce parts and prototypes. During this process, the machines follow a set of instructions that are pre-programmed through specialized software. These instructions are translated into a machine language called G-codes, which tell the machines how to perform each task. CNC operations can take place on a variety of materials, including metals, woods, and plastics.
The process starts when a 3D model of the desired part is created in CAD software. The file is then uploaded into a CAM program, which extracts the geometry of the design and generates the digital programming code that will control the CNC machine and manipulate its tooling to produce the custom-designed part. The CAM program also generates the G-codes that control the machine’s movement, which are based on the 3D model.
The machine then uses the G-codes to move around the material and make cuts, producing the desired shape. Depending on the type of part, these movements can be along linear or rotary axes. Some machines use both types of axes, while others are dedicated to one or the other. For example, a cutting machine will have two linear axes while a milling machine will have at least three – X, Y, and Z.
CNC machines are highly accurate, and they can produce cuts that are a fraction of the width of a human hair. However, there is still some variability between duplicates, so it is important to carefully specify tolerances when submitting parts for machining.