The global economic landscape is reshaping itself under the weight of geopolitical tensions, and nowhere is this more visible than in the arena of global trade. The imposition of tariffs by the Trump administration on Chinese goods aimed to correct trade imbalances but left US businesses navigating turbulent waters. This article delves into how these tariffs have affected US businesses, focusing on both the direct impacts and broader economic implications.
The Ripple Effect of Tariffs on US Manufacturing
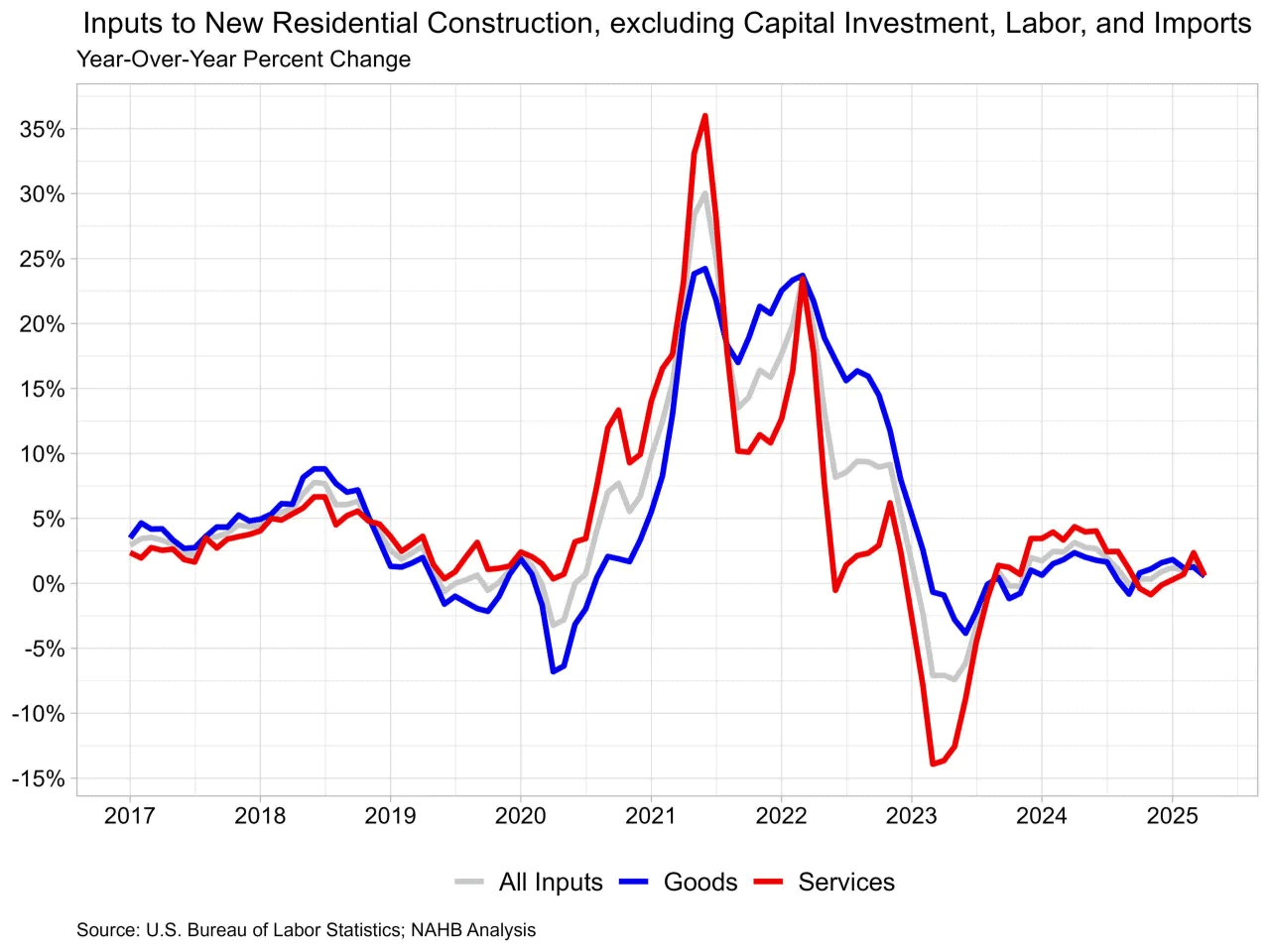
The tariffs imposed on Chinese imports included a wide array of products, from raw materials to finished goods. This has left a mark on the US manufacturing sector, which is heavily reliant on Chinese imports for critical components.
Supply Chain Challenges
One of the most significant impacts has been the disruption of supply chains. Businesses have faced:
- Increased Costs: The tariffs led to higher import duties on essential components, escalating production costs for manufacturers who rely on Chinese goods.
- Inventory Delays: Delays in receiving critical components due to the uncertainties surrounding tariffs have caused slowdowns in production schedules.
Impact on Business Strategies
In facing these challenges, many companies have been forced to revisit their business strategies. Some of the common adjustments include:
- Rethinking Sourcing: Businesses are exploring alternative sourcing options, such as looking for suppliers in countries not affected by tariffs.
- Price Adjustments: To offset increased costs, some companies have had to raise prices, which can hurt competitiveness and demand.
A Strain on Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
While large corporations often have the resources to absorb increased costs or relocate their supply chains, SMEs face distinct challenges.
Financial Pressures
Tariffs add a financial burden that many small businesses find challenging to manage:
- Reduced Profit Margins: SMEs frequently operate with thinner profit margins, making them less capable of absorbing additional costs.
- Higher Operational Costs: For many, the tariffs translate to higher expenses across the board, from materials to shipping, squeezing their financial flexibility.
Adaptation and Innovation
Despite the challenges, some SMEs are turning to innovation and adaptation to survive:
- Product Diversification: Small businesses are increasingly diversifying their product offerings to reduce dependency on any single market.
- Investing in Technology: SMEs are adopting new technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs, helping them adapt to the new economic environment.
Economic Implications and Future Outlook
The effects of tariffs are not confined to individual businesses but extend to the broader economy. Understanding these implications can provide insights into the future of US trade and business resilience.
Impact on Consumer Prices
With increased costs of production, consumers are witnessing higher prices on various goods. This inflationary pressure affects:
- Consumer Purchasing Power: As prices rise, consumers may reduce spending, affecting overall economic demand.
- Market Inflation: Sustained price increases contribute to broader inflation trends, impacting economic stability.
Trade Relations and Economic Policies
The imposition of tariffs has influenced international relations and economic policies:
- Global Trade Relations: The tension between the US and China has prompted questions about the future of global trade dynamics and the role of international trade agreements.
- Policy Adjustments: The government is under pressure to balance protectionist policies with the need to foster international economic cooperation.
Strategies for Surviving and Thriving
Faced with these challenges, businesses across sectors are developing strategies to weather the storm and emerge more resilient.
Leveraging Domestic Opportunities
Increasing focus on domestic opportunities can help businesses reduce reliance on international imports:
- Domestic Sourcing: Investing in local supply chains not only reduces dependency on foreign imports but also supports the national economy.
- Government Incentives: Businesses should explore available government incentives aimed at boosting domestic production and innovation.
Building Resilient Business Models
Resilience is key to navigating market uncertainties:
- Agile Operations: Businesses should focus on building agile and flexible operations that can quickly adapt to changing conditions.
- Market Diversification: By tapping into diverse markets, companies can insulate themselves from localized disruptions.
Conclusion
Navigating the complex terrain of tariffs and economic challenges is no small feat for US businesses. While costs and operational challenges present hurdles, they also encourage innovation and adaptation. By investing in domestic opportunities, adopting resilient business models, and harnessing the power of innovation, US companies can not only survive but thrive in this new economic landscape.
As the dust settles on the ongoing trade discussions and negotiations, it is clear that the path to economic stability involves balancing protectionism with open market policies, ensuring that American businesses remain competitive on the global stage.